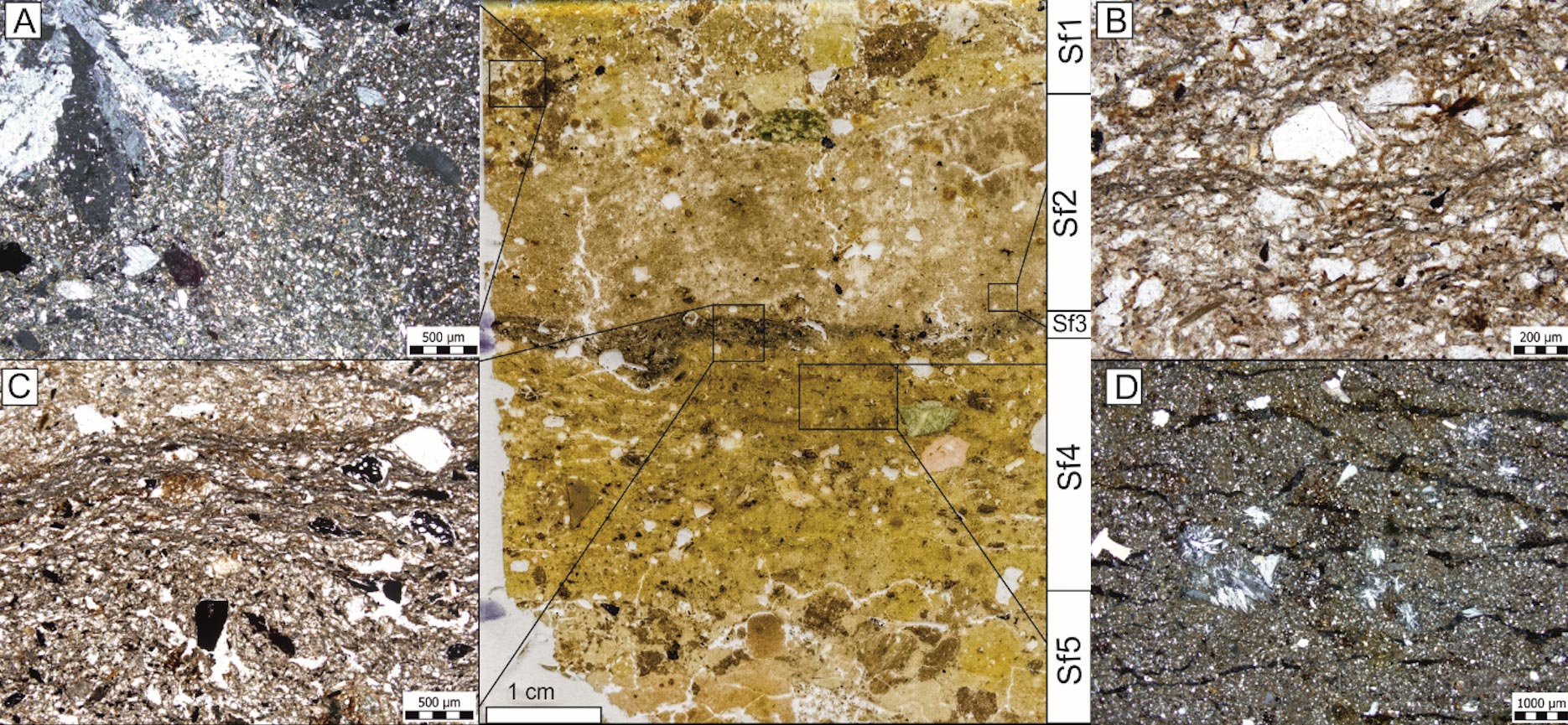
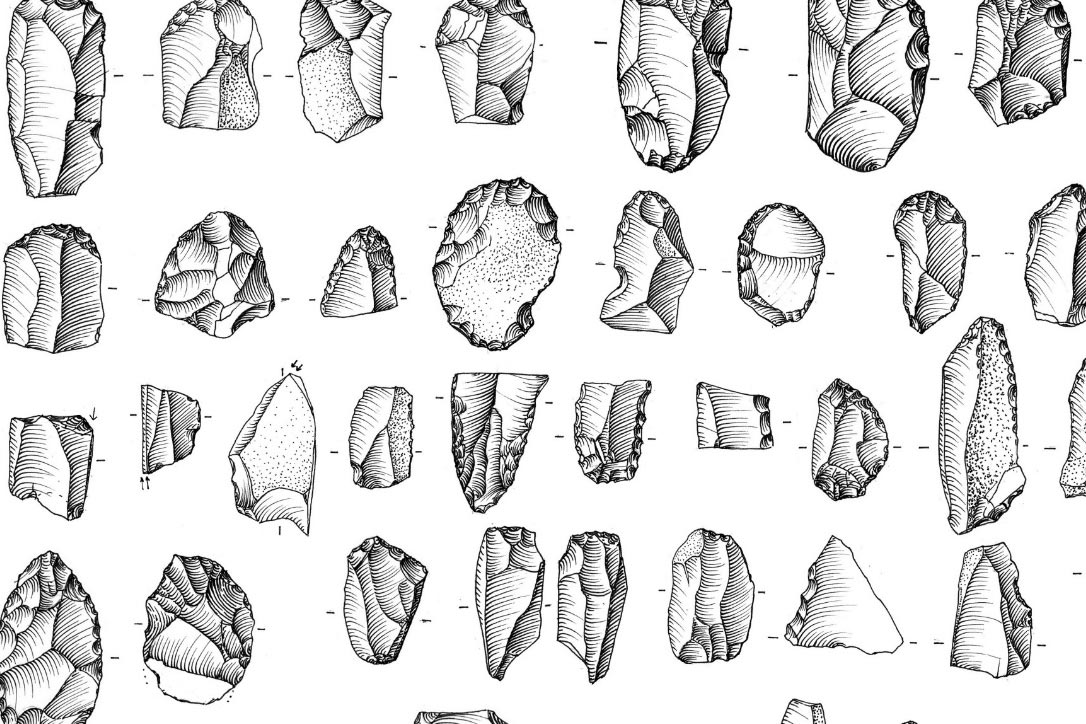
Human teeth cementum and dentin microstructures analysis
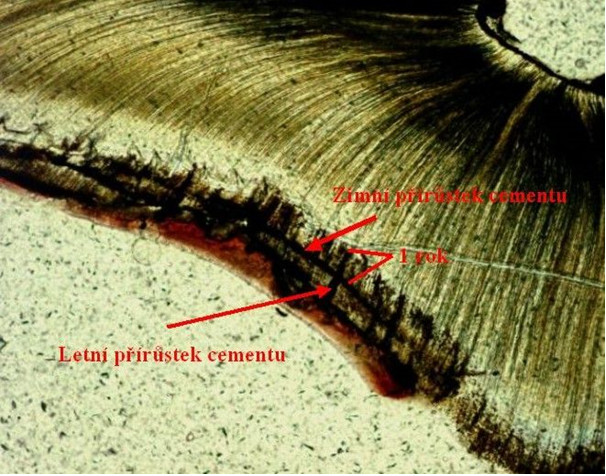
Teeth cementum microstructures analysis is often used for an age determination of humans and animals. The cementum grows during the entire life of an individual. The cementum growths are studied on thin sections, which are made in the first third of a tooth root. Roots...